What Does Coffee Taste Like?
The flavor of coffee is the result of various taste sensations, from its initial aroma to the lingering aftertaste. Several factors can influence how we perceive coffee flavor, including the temperature of the brew. In fact, the main flavor characteristics of coffee can change as it cools.
Coffee beans and roasted coffee contain over 800 different chemical compounds, each contributing to the unique taste and aroma. Some of the most important molecules include carbonyls, phenols, esters, and pyrazines. While you don’t need a deep understanding of chemistry to enjoy coffee, knowing the key flavor characteristics—aroma, sweetness, acidity, bitterness, and aftertaste—can enhance your appreciation for this beloved beverage.
Aroma
Aroma is one of the most significant factors influencing how we perceive flavor. In fact, our sense of smell plays a bigger role in taste than most people realize. Olfactory neurons, located in the nasal cavity, detect odor molecules and send signals to the brain about what we’re smelling. If you have a blocked nose, it can reduce your ability to fully experience the taste of coffee.

Olfactory receptor neurons are located in a small area at the top of the nasal cavity / Source: bio.libretexts.org
Coffee’s aroma is shaped by its chemical composition. For instance, pyrazines contribute grassy or earthy notes, while pyridines add fruity or floral aromas. Lipids and oils in coffee can bring out nutty or chocolatey flavors.
Many factors affect a coffee’s aroma, including the origin of the beans (country, region), coffee variety, growing conditions, processing methods (wet or dry), roasting level, and brewing techniques.
Sweetness
Although coffee itself isn’t naturally sweet, it’s often described with flavors like caramel or chocolate—associations made during the roasting process. Roasting caramelizes the sugars in coffee beans, creating a sweet taste. Beans with higher density often intensify this sweetness.
During roasting, most of the sugars in coffee break down, leaving the final beverage with a low sugar content. However, the perceived sweetness helps balance other flavors in the cup, creating a well-rounded taste.
Acidity
Acidity in coffee brings brightness and liveliness to the cup. It can give coffee a juicy or fruity flavor, often described as having berry-like or citrusy notes. However, acidity should be balanced with other flavor characteristics like sweetness or bitterness to avoid overwhelming the palate.
Coffee beans contain various acids that contribute to their flavor. As beans are roasted, some acids break down, while others remain, influencing the overall taste. Coffees known for high acidity, such as those from Kenya and Colombia, are typically grown at high altitudes, often in shaded areas. These regions produce beans with vibrant, fruity flavors and pronounced acidity.
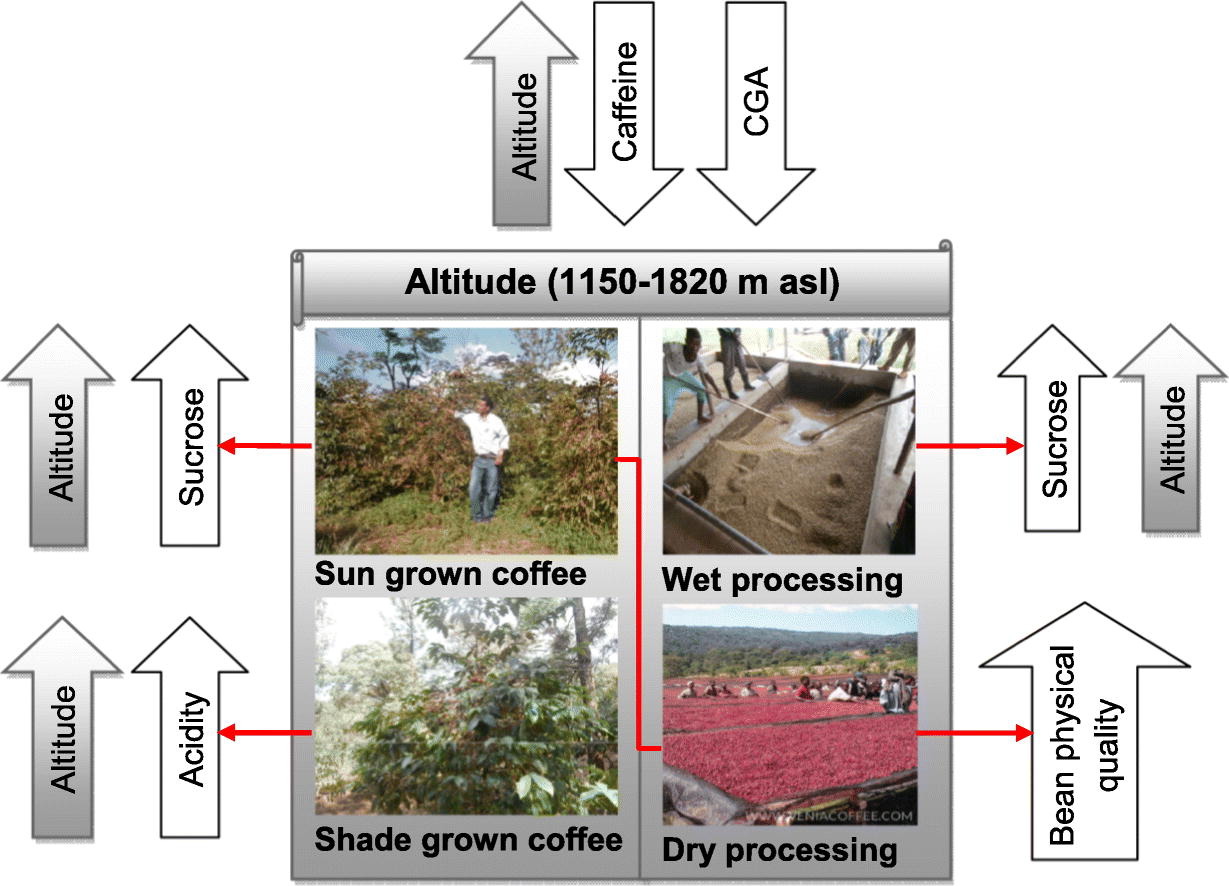
The Impact of Altitude on the Biochemical Composition and Quality of Green Arabica Coffee Beans / sciencedirect.com
During roasting, acidity decreases as beans undergo caramelization and the breakdown of organic acids. Green coffee beans start with a pH level of around 5.8, but after roasting, the acidity can drop to pH 4.8 by the time the beans hit the first crack (a key roasting stage at around 205-210°C).
Bitterness
While bitterness is often blamed for unpleasant coffee, it’s not always the culprit. Some flavors attributed to bitterness may actually be sourness or acidity. In espresso drinks, bitterness can also come from improperly steamed milk.
The bitterness in coffee comes from compounds formed during roasting, including trigonelline, cinnamic acid, and caffeine. Bitterness can balance other flavors, enhancing sweetness and softening acidity, contributing to a more complex flavor profile.
However, too much bitterness can be a sign of over-extraction, which occurs when coffee is brewed for too long or the grind size is too fine. On the flip side, under-extraction results in less bitterness and a weaker flavor.
Aftertaste
The aftertaste is the flavor that lingers in your mouth after you’ve finished drinking coffee. It can last anywhere from a few minutes to much longer, depending on the coffee. Aftertastes may be fruity, citrusy, nutty, chocolatey, or caramel-like, similar to the coffee’s original flavor.
The aftertaste also comes with other sensations, such as astringency, warmth, or coolness, which contribute to the overall experience of drinking coffee.
Why Understanding Coffee Flavor Matters
Knowing the key flavor characteristics of coffee can help you brew the perfect cup tailored to your preferences. You can adjust factors like the grind size, brewing method, and coffee-to-water ratio to enhance specific flavors.
Moreover, coffee is more than just a beverage for many people—it’s a conversation starter, a hobby, and even a competitive art. Coffee tasting, or cupping, is a popular activity for both professionals and enthusiasts, where participants describe the taste of coffee in detail. Many countries even hold championships where tasters showcase their ability to discern subtle flavor notes.