What Does Coffee Taste Like?
Coffee flavor is the outcome of all the taste sensations from aroma to the final aftertaste. There are many factors that can influence the perception of coffee taste, including the temperature of the drink. The main descriptor in the flavor can change as the coffee cools down.
Coffee beans and roasted coffee contain more than 800 different chemical compounds that can affect their flavor and aroma. Among these, the most important molecules that determine coffee taste are carbonyls, phenols, esters, and pyrazines. However, you don’t need to have expensive equipment or a PhD in chemistry to begin to understand the flavor of coffee. It’s enough to know which characteristics you need to pay attention to. We shall discuss the most important ones: aroma, sweetness, acidity, bitterness, and aftertaste.
Aroma
When it comes to taste, the sense of smell plays a vital role. In fact, most researchers agree that it’s the sense of smell that has the greatest impact on how we perceive flavor.
The neurons responsible for our sense of smell, known as olfactory neurons, are responsible for much of the sensation we experience when we drink or eat. When we inhale air, odor molecules bind to these neurons, which then send signals to the brain about what we’re smelling. If we have a stuffy nose, it can interfere with our sense of smell and reduce our ability to fully perceive the taste.

Olfactory receptor neurons are located in a small area at the top of the nasal cavity / Source: bio.libretexts.org
The different chemical compounds present in coffee play a significant role in creating its unique aroma. Pyrazines contribute to the grassy and earthy tones, while pyridinines are responsible for fruity and floral notes. Lipids and oils can give coffee a nutty or chocolaty aroma.
The origin of coffee beans, such as the country and region of their cultivation, the coffee variety, the growing conditions, the processing methods (wet or dry), the degree of roasting, and the preparation methods can all have a considerable impact on the coffee aroma, which can vary significantly.
Sweetness
Many people describe the flavor of coffee using words like caramel or chocolate, which are typically associated with sweetness. However, coffee itself is not naturally sweet. Rather, it is the roasting process that gives coffee its unique sweet taste. Additionally, the higher density of the coffee beans further intensifies this sensation. Understanding the sweetness of coffee can help you better appreciate and evaluate the overall balance of flavors in the beverage.
During the roasting process of coffee beans, high temperatures are applied which cause the sugars within the beans to break down or convert into other compounds. Consequently, the sugar content in roasted coffee beans is significantly reduced as compared to unroasted ones. As a result, the final beverage contains even less sugar.
Acidity
Acidity is an important factor in coffee that adds a fresh flavor to the beverage. It also affects the perception of its texture. The flavor of coffee can be described with words like juicy, fruity or berry, which is due to the presence of different acids. However, it is important to consider the balance of these acids with other flavor characteristics such as bitterness or sweetness.
Roasted coffee is composed of various acids, which contribute to its flavor. However, these acids are balanced out by other flavor elements in coffee, resulting in a smooth taste. For instance, bitterness can offset acidity, creating a complex and well-rounded flavor profile.
Coffees that are known for their high acidity are usually grown at high altitudes in shaded areas. Nonetheless, altitude has not been found to have a significant impact on the acidity of coffees grown in non-shaded areas. Some growers, such as those from Kenya and Colombia, are renowned for producing coffees that have vibrant flavors and pronounced acidity.
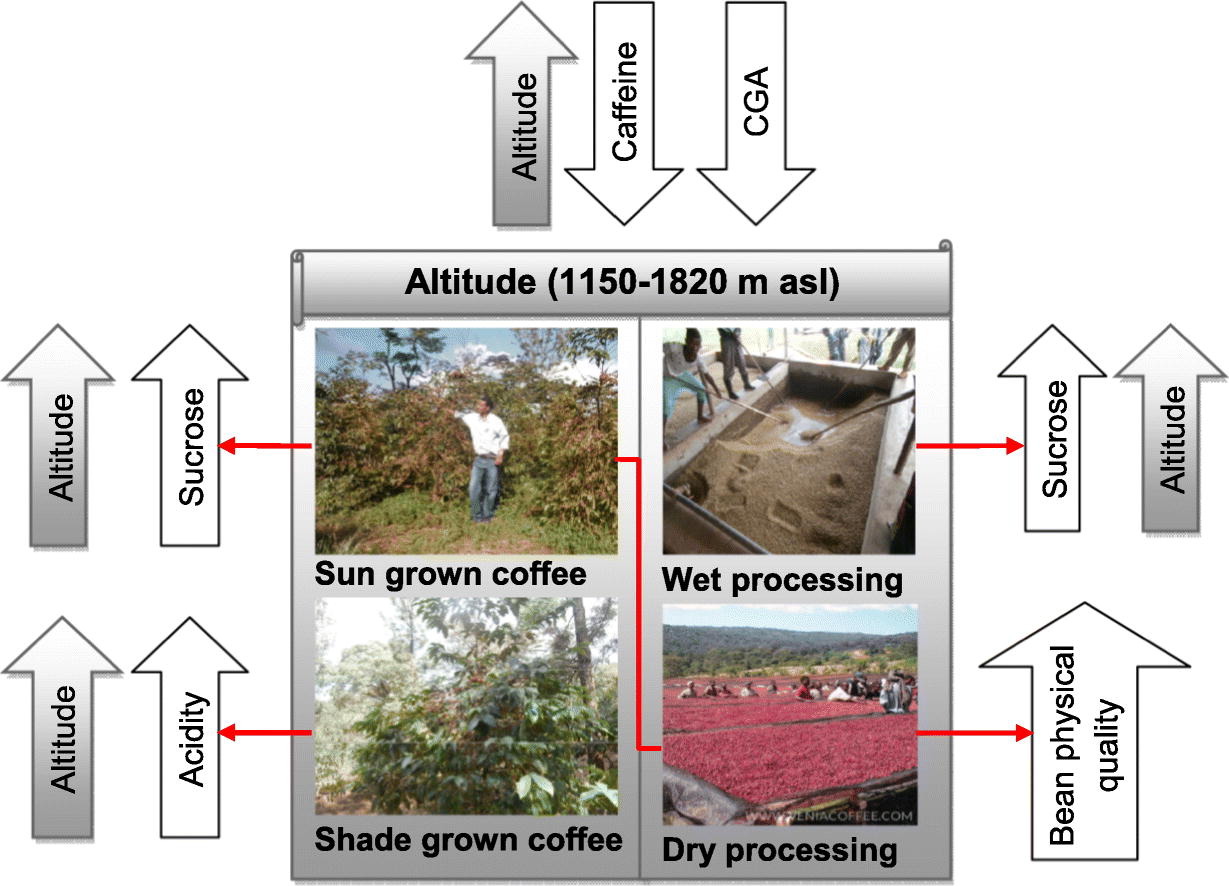
The Impact of Altitude on the Biochemical Composition and Quality of Green Arabica Coffee Beans / sciencedirect.com
During the roasting process, coffee beans undergo various chemical changes that significantly alter their acidity. These changes are a result of caramelization and degradation of organic acids. Initially, the green coffee beans have a high acidity level, usually around pH 5.8. However, as the beans are roasted, the acidity decreases. The first critical point in coffee roasting is called the “first crack,” which occurs at a temperature of about 205-210 degrees Celsius. By the end of the first crack, the acidity is usually reduced to pH 4.8.
Bitterness
It is common for people to attribute any flaws in a beverage to its bitterness. For example, when people taste unpleasant coffee, they often say that it is too bitter. However, this answer may not be entirely accurate, because the flavor sensation that people generally refer to as bitterness is actually often tartness or acidity. In the case of espresso-based drinks, the bitterness may be due to improperly whipped milk.
Bitterness in coffee is caused by the complex interaction of various chemical compounds that are present in coffee beans and are formed during roasting. Trigonelline, cinnamic acid, and caffeine, which were once thought to be tasteless, are primarily responsible for the bitterness in coffee.
When it comes to coffee, bitterness can actually enhance the sweetness and balance out unwanted acidity. It serves to structure the flavor profile, bringing together all the various elements into a harmonious whole.
However, a bitter taste in coffee often indicates over-extraction. This means that if you extract too much from your espresso or brew your French press for too long, you’ll end up with a batch of bitter coffee. On the other hand, if you extract too little, you’ll get a less bitter version.
Aftertaste
The taste sensation that lingers in your mouth after you’ve finished drinking coffee is known as the coffee aftertaste. This aftertaste can vary in length and can stay in your mouth for several minutes or even longer.
The coffee aftertaste is composed of different flavors that can be similar to the taste of the coffee itself. These may include fruity, citrus, nutty, chocolate, or caramel flavors.
Apart from flavor, the coffee aftertaste may also be accompanied by other sensations such as astringency, warmth, or coolness, which can contribute to the overall experience of the beverage.
Why is it important to understand the taste of coffee?
Understanding the taste of coffee can be helpful in preparing a perfect cup of coffee that suits your preferences. You can adjust the grind, the brewing method, and change the coffee and water proportions accordingly. Knowing your desired flavor of coffee will make it easier for you to choose the right water and coffee beans.
Moreover, for many people, coffee is not just a beverage, but also a topic of discussion and socializing. Besides coffee cupping, which is often attended by professionals and amateurs alike, many countries hold championships where participants describe the taste of coffee in detail.